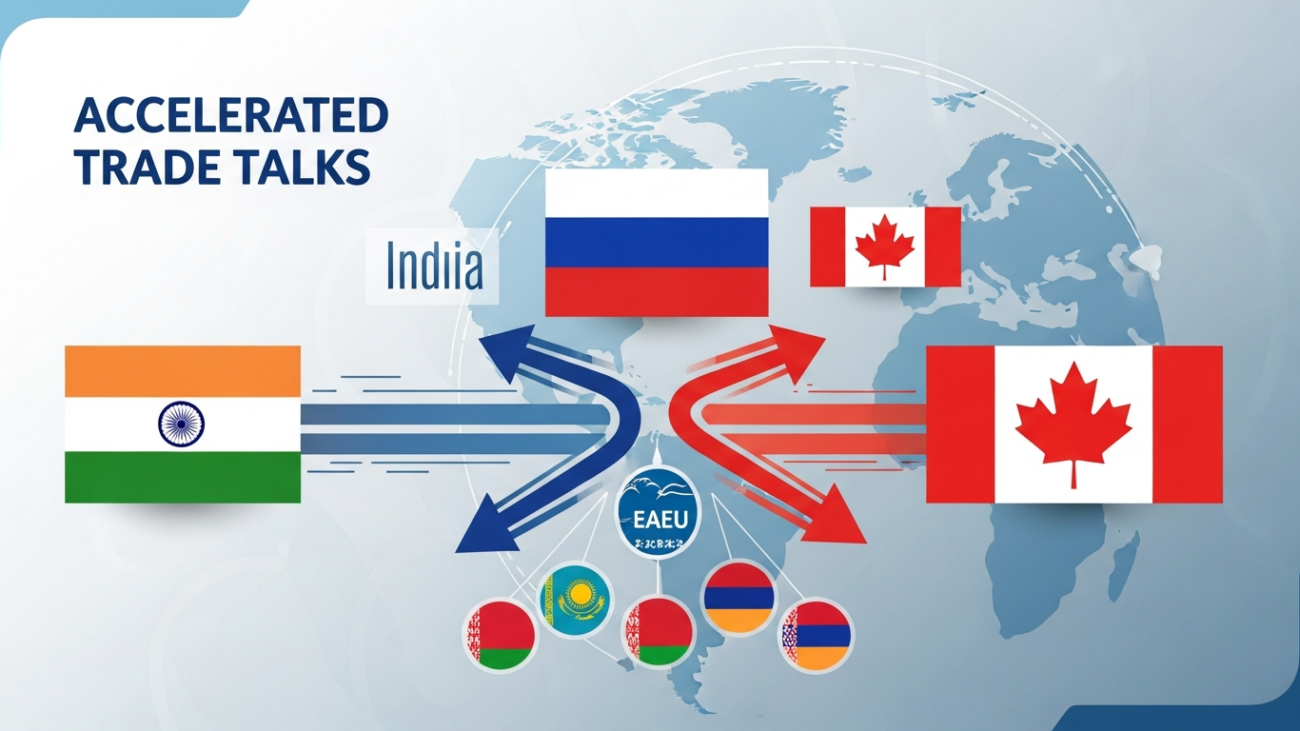
GLOBAL! India 2 FTAs Surge: EAEU & Canada Trade Policy Shocks
The first week of December 2025 was dominated by India’s assertive diplomatic drive to diversify its global trade footprint, a strategic necessity given the lingering uncertainty surrounding the US-India tariff dispute. High-level summitry with Russia and a significant thaw in relations with Canada led to formal mandates to fast-track major Free Trade Agreements (FTAs).
For The Exporter Hub and its members, these developments signal concrete pathways to new, large markets, offering stability and growth potential outside traditional Western trade channels.
1. 🇷🇺 India-Russia Summit: Fast-Track Mandate for EAEU FTA
The most defining event was the 23rd India-Russia Annual Summit in New Delhi (December 4-5, 2025), where the leadership of both nations provided a powerful mandate to finalize the Free Trade Agreement (FTA) with the Russia-led Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU).
-
Fast-Tracking Negotiations: Prime Minister Narendra Modi and President Vladimir Putin directed officials to “intensify efforts in negotiations” for the early conclusion of the FTA on goods between India and the five-member EAEU (Russia, Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan).
-
Trade Deficit Solution: A core objective of the FTA is to boost India’s exports to Russia, addressing the current significant trade imbalance. Key Indian sectors being prioritized in the negotiations include pharmaceuticals, chemicals, engineering goods, machinery, and agricultural/marine products.
-
Operational Focus: Beyond tariffs, the summit focused on resolving practical trade hurdles, including:
-
Developing systems for bilateral settlements using national currencies to ensure smooth payments.
-
Addressing non-tariff barriers, such as listing procedures for marine exports and registration requirements for pharmaceuticals in EAEU markets.
-
-
Target: The leaders reaffirmed the ambitious goal of reaching $100 billion in bilateral trade by 2030.
2. 🇨🇦 India Resumes CEPA Talks with Canada after Diplomatic Thaw
In a significant sign of mended relations, India and Canada announced the resumption of talks for a Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA), which had been on pause since 2023.
-
Restart of Discussions: Following high-level meetings, the countries agreed to formally restart discussions on an ambitious CEPA, signaling a mutual recognition that trade and talent flows are essential to both economies.
-
Strategic Trade Focus: The resumption is motivated by a desire to boost two-way trade significantly and secure key strategic resources. India is keen on accessing critical minerals (like Uranium) and processing technologies from Canada, while Canada seeks broader market access in India.
-
Timeline and Scope: Officials are reportedly aiming for an early-progress agreement covering services, digital trade, and the temporary entry of highly skilled workers by mid-2026, ahead of a fuller goods accord. This will be a major relief for the large Indian diaspora and the tech sector.
3. ⚠️ WTO Issues Warning on Global Trade Slowdown
Amid the bilateral trade push, the World Trade Organization (WTO) released data highlighting a deceleration in global goods trade, largely driven by the fading effects of tariff-related front-loading.
-
Trade Growth Moderation: The WTO’s goods barometer dropped to $\text{101.8}$, signaling a cooling-off in the transportation of goods worldwide. While still indicating expansion, the pace is slowing.
-
The Tariff Factor: This moderation is directly attributed to the end of the “front-loading” of imports—where US companies accelerated orders in early 2025 to avoid new tariffs. The WTO maintains its sharply reduced forecast of just $0.5% global trade growth for 2026, underscoring that the full, negative impact of trade barriers is yet to be fully realized.
-
Supply Chain Diversion: The report noted that while US imports from China dropped significantly, imports from countries like India, Vietnam, and Thailand increased by over $\text{20\%}$, confirming the ongoing supply chain diversification driven by tariffs.
4. 🇮🇳 India’s Policy Direction: Defensive and Diversified
The week’s developments underscore India’s shift from a purely defensive trade posture to an active, diversified, and strategic engagement approach, as outlined in its long-term Foreign Trade Policy (FTP).
-
Countering Risk: By aggressively pursuing FTAs with blocs like the EAEU and individual countries like Canada, India is attempting to de-risk its export strategy and build resilient supply chains that are less exposed to the geopolitical volatility affecting US and European markets.
-
Sectoral Focus: The focus on non-tariff barriers and specific sectors like pharmaceuticals and engineering goods in the EAEU talks demonstrates a pragmatic, export-centric policy implementation to quickly realize market opportunities for Indian MSMEs.
Source : www.mea.gov.in


Add a Comment