Table of Contents
Introduction: Why Importing from India?
In the global marketplace, India has emerged as a powerhouse for sourcing a wide range of products, from building materials to textiles, chemicals, and engineering goods. With its vast manufacturing capabilities, competitive labor costs, and a government increasingly focused on ease of doing business, India offers a compelling proposition for importers worldwide. However, navigating the import process can seem complex, particularly for first-time importers.
This comprehensive guide will break down the entire process into a simple, step-by-step roadmap. Whether you are a small business owner looking to diversify your supply chain or a large corporation seeking a reliable partner, this article will equip you with the knowledge to import goods from India smoothly and efficiently.

The Foundation: Essential Preparations Before You Begin
Before you place your first order, a few critical steps are necessary to ensure a seamless and legal import process.
- Obtain Your Importer-Exporter Code (IEC): This is the most crucial step. In India, an IEC is a 10-digit unique code issued by the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) that is mandatory for any business involved in importing or exporting. It is a one-time registration and has lifetime validity. You will need a PAN card and proof of your business address to apply. Without an IEC, your shipment will not be cleared by Indian Customs.
- Product and Market Research: Identify the specific product you want to import. A successful import business starts with a high-demand, profitable product. Conduct thorough market research to understand the demand, potential competition, and any specific regulatory requirements for your product in your country.
- Find a Reliable Supplier: This is a make-or-break step. Use reputable B2B platforms like TheExporterHub.com, attend trade fairs, and leverage professional networks to find a trustworthy and certified supplier. Perform due diligence on potential suppliers by checking their business credentials, production capacity, and quality certifications. Don’t hesitate to request product samples before finalizing a deal.

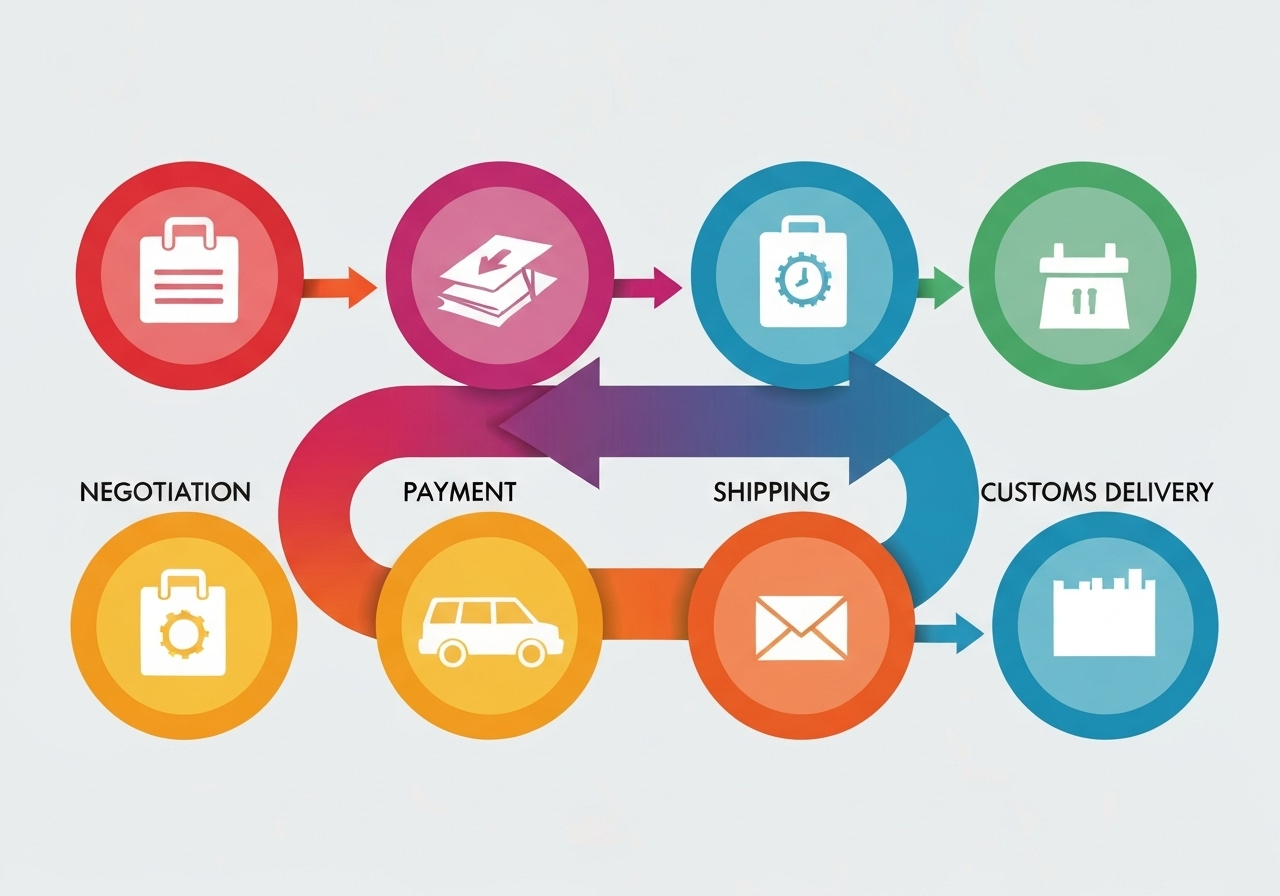
The Core Process: A 5-Step Roadmap to Importing
With your preparations complete, you are ready to execute the import transaction.
Step 1: Negotiate and Finalize the Deal Once you have selected a supplier, negotiate the terms of the sale. This includes the price, quantity, quality standards, and, most importantly, the Incoterms® (International Commercial Terms). Incoterms, such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), define who is responsible for the goods at each stage of the journey. Ensure all terms are clearly laid out in a legally binding contract or purchase order.
Step 2: Place Your Order and Arrange Payment Send a formal Purchase Order (PO) to your supplier. When it comes to payment, there are several common methods:

- Advance Payment: The safest option for the supplier, but risky for the importer.
- Letter of Credit (LC): A highly secure method where a bank guarantees payment to the supplier after all contract conditions are met. This is often preferred for large transactions.
- Documents Against Payment (D/P) or Documents Against Acceptance (D/A): A bank-mediated process that releases documents to the importer only after payment or acceptance of a Bill of Exchange.
Step 3: Shipping and Logistics Your supplier will prepare the goods for shipment. You will need to decide on the mode of transport: sea freight (for large, heavy shipments), air freight (for urgent or high-value goods), or land transport (for shipments to neighboring countries). A reliable freight forwarder or logistics partner is essential to handle the booking, transportation, and tracking of your consignment.
Step 4: Customs Clearance at the Destination Port This is a critical stage. The freight forwarder or a customs broker will file a Bill of Entry with the customs authority of your country. This document contains all the details of the imported goods and is used for assessment of customs duties. Your goods will be inspected and verified against the documents provided.
Step 5: Receive Your Shipment Once customs clearance is complete and all duties and taxes are paid, your goods will be released. You or your logistics partner can then arrange for the final delivery of the goods from the port to your warehouse or specified location.
Navigating the Paperwork: The Essential Documents
Documentation is the backbone of international trade. Missing or incorrect documents can lead to significant delays and penalties. Make sure you have the following ready:
- Commercial Invoice: A bill of sale from the supplier to the importer, detailing the goods, quantity, and price.
- Packing List: Provides a detailed inventory of the contents of each package in the shipment.
- Bill of Lading (B/L) or Air Waybill (AWB): A legal document issued by the carrier confirming receipt of the goods for shipment.
- Bill of Entry: Filed by the importer or their agent with customs to declare the goods and pay duties.
- Certificate of Origin (CoO): Certifies that the goods were manufactured or processed in India. This may be required to claim preferential tariffs under a Free Trade Agreement.
- Insurance Certificate: Proof that the goods are insured during transit.
- Purchase Order: Your formal request for the goods from the supplier.

Overcoming Common Challenges
Importing can have its hurdles, but a proactive approach can mitigate risks.
- Currency Fluctuations: Fluctuation in the exchange rate between your currency and the Indian Rupee (INR) can impact your profit margins. Consider using foreign exchange hedging strategies or fixing the price with your supplier in a stable currency.
- Regulatory Complexity: India’s regulatory landscape is constantly evolving. Staying updated on new policies, tariffs, and product-specific restrictions is crucial. Working with a knowledgeable local agent or customs broker is highly recommended.
- Logistics and Delays: Unforeseen shipping delays, port congestion, or supply chain disruptions can happen. Use a freight forwarder with a strong track record and robust tracking systems.

Pro-Tips for a Successful Import Operation
Build a Strong Relationship: Cultivate a good working relationship with your supplier and logistics partners. Trust and open communication can resolve issues quickly.
Calculate Total Landed Cost: Don’t just focus on the product price. Calculate all costs, including shipping, insurance, customs duties, taxes, and handling fees, to determine your true cost and profitability.
Leverage Technology: Use digital platforms for communication, document sharing, and tracking to streamline your operations.

Conclusion
Importing from India offers a world of opportunities for businesses seeking high-quality, competitively priced products. While the process involves multiple steps and requires careful planning, it is highly manageable with the right preparation and knowledge. By following this guide, you can navigate the complexities of international trade and build a thriving import business.
Ready to find your perfect supplier? Explore thousands of verified exporters on TheExporterHub.com and get your first Request for Quote submitted today.


Add a Comment